Pololu Metal DC Gearmotors » 25D Metal Gearmotors » 6V Low-Power (LP) 25D mm Gearmotors »
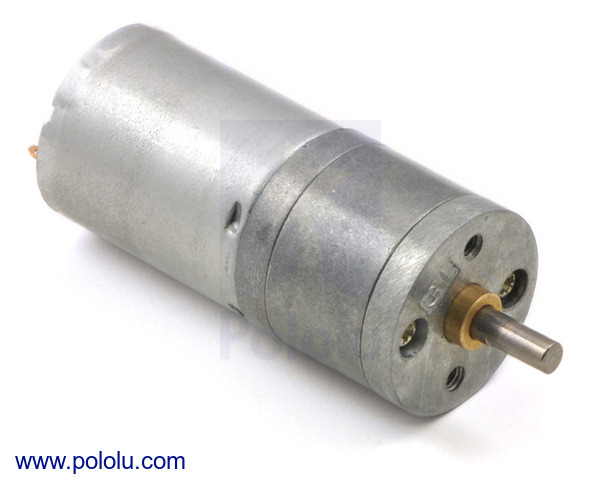
4.4:1 Metal Gearmotor 25Dx48L mm LP 6V
This gearmotor consists of a low-power, 6 V brushed DC motor combined with a 4.4:1 metal spur gearbox. The gearmotor is cylindrical, with a diameter just under 25 mm, and the D-shaped output shaft is 4 mm in diameter and extends 12.5 mm from the face plate of the gearbox. This gearmotor is also available with an integrated encoder.
Key specifications:
| voltage | no-load performance | stall extrapolation |
|---|---|---|
| 6 V | 1300 RPM, 100 mA | 0.63 kg⋅cm (8.7 oz⋅in), 2.0 A |
Alternatives available with variations in these parameter(s): gear ratio motor type encoders? Select variant…
 Compare all products in 6V Low-Power (LP) 25D mm Gearmotors.
Compare all products in 6V Low-Power (LP) 25D mm Gearmotors.
| Description | Specs (16) | Pictures (10) | Resources (3) | FAQs (3) | On the blog (0) | Distributors (0) |
|---|
Dimensions
| Size: | 25D x 48L mm1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 82 g |
| Shaft diameter: | 4 mm2 |
General specifications
| Gear ratio: | 4.4:1 |
|---|---|
| No-load speed @ 6V: | 1300 rpm3 |
| No-load current @ 6V: | 0.10 A4 |
| Stall current @ 6V: | 2.0 A5 |
| Stall torque @ 6V: | 0.63 kg·cm5 |
| Max output power @ 6V: | 2.1 W |
| Motor type: | 6V, 2.0A stall (LP 6V) |
Performance at maximum efficiency
| Max efficiency @ 6V: | 49 % |
|---|---|
| Speed at max efficiency: | 1100 rpm |
| Torque at max efficiency: | 0.082 kg·cm |
| Current at max efficiency: | 0.32 A |
| Output power at max efficiency: | 0.94 W |
General specifications
| Encoders?: | N |
|---|
Notes:
- 1
- Length measurement is from gearbox face plate to back of motor (it does not include the output shaft or motor terminals). See dimension diagram for details.
- 2
- D shaft.
- 3
- Typical; ±20%.
- 4
- Typical, ±50%; no-load current depends on internal friction, which is affected by many factors, including ambient temperature and duration of motor operation.
- 5
- Stalling is likely to damage the gearmotor. Stall parameters come from a theoretical extrapolation of performance at loads far from stall. As the motor heats up, as happens as it approaches an actual stall, the stall torque and current decrease.