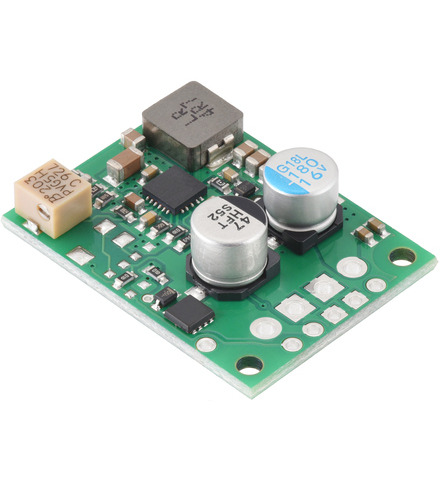
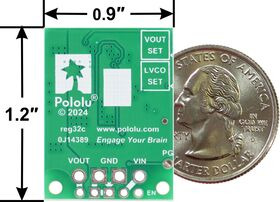
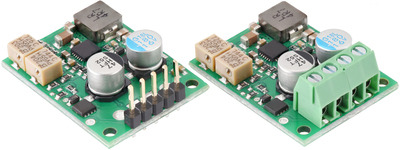
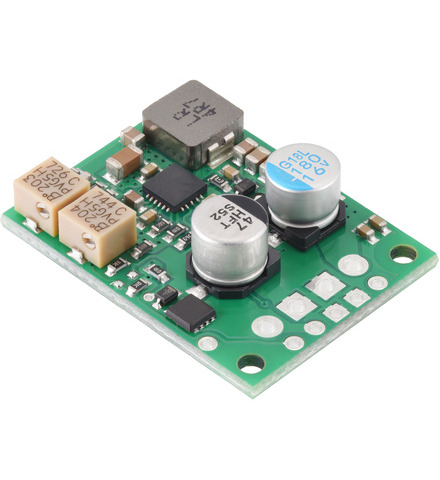
The D30V33MAx family of buck (step-down) voltage regulators are larger, adjustable-output members of the broader D30V3x line of synchronous regulators that have through-holes for both 0.1″ headers and for 3.5mm-pitch terminal blocks.
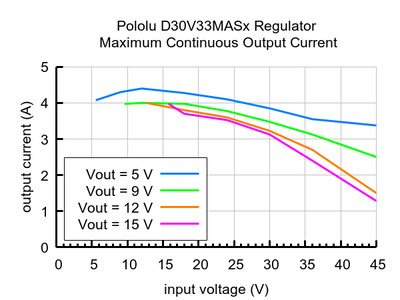
They generate lower output voltages from input voltages as high as 45 V and can typically support continuous output currents between 1.3 A and 4.5 A, depending on the input voltage and output voltage. They also have very low dropout voltages.
| Regulator |
Output voltage |
Typical max
output current1 |
Input voltage2 |
Adjustable
low-voltage
cutoff |
Size |
Price |
|
| #4853: D30V33MAL |
1.4 V – 7 V |
3.8 A |
3.3 V – 45 V |
– |
0.9″ × 1.2″ |
$25.95 |
| #4852: D30V33MALCMA |
|
$29.95 |
| #4855: D30V33MAS |
4.2 V – 15 V |
3.3 A |
4.2 V – 45 V |
– |
$25.95 |
| #4854: D30V33MASCMA |
|
$29.95 |
| 1At 30 V in. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input and output voltages and is limited by thermal dissipation. |
| 2Operating voltage must be higher than the set output voltage and is subject to dropout voltage considerations. |
| 1.4-7V, 3.8A D30V33MALx |
4.2-15V, 3.3A D30V33MASx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The output voltage is precision adjustable through an 11-turn potentiometer, and each version is available with or without an adjustable low-voltage cutoff (also set through a precision 11-turn potentiometer).
The regulators have reverse voltage protection up to 40 V, input under-voltage lockout, over-current protection, and short-circuit protection. A thermal shutdown feature also helps prevent damage from overheating and a soft-start feature limits the inrush current and gradually ramps the output voltage on startup.
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category
Products in category “D30V33MAx Fine-Adjust Voltage Regulators”
| Output voltage range |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
Low-voltage cutoff |
| 1.4 V – 7 V |
3.8 A |
3.3 V – 45 V |
adjustable |
Note 1: At 30 V in and 3.3 V out. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input and output voltages and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graph on the product page for more information.
Note 2: Input voltage must be higher than the output voltage and is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage range |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
Low-voltage cutoff |
| 1.4 V – 7 V |
3.8 A |
3.3 V – 45 V |
none |
Note 1: At 30 V in and 3.3 V out. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input and output voltages and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graph on the product page for more information.
Note 2: Input voltage must be higher than the output voltage and is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage range |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
Low-voltage cutoff |
| 4.2 V – 15 V |
3.3 A |
4.2 V – 45 V |
adjustable |
Note 1: At 30 V in and 9 V out. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input and output voltages and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graph on the product page for more information.
Note 2: Input voltage must be higher than the output voltage and is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage range |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
Low-voltage cutoff |
| 4.2 V – 15 V |
3.3 A |
4.2 V – 45 V |
none |
Note 1: At 30 V in and 9 V out. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input and output voltages and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graph on the product page for more information.
Note 2: Input voltage must be higher than the output voltage and is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category