Pololu Blog »
New product: Breakout Board for microSD Card
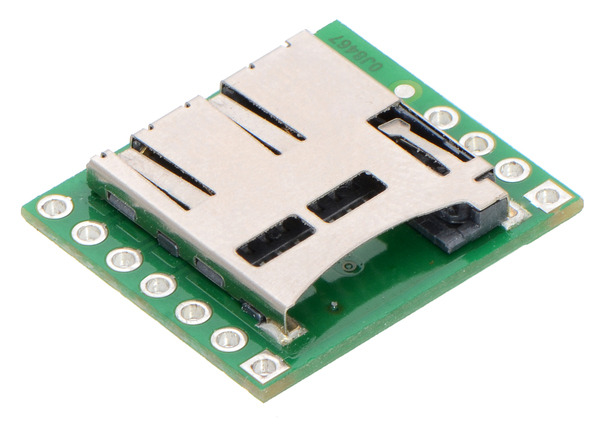
Last week, Jon mentioned how several of the mechanical engineers here at Pololu were assigned a simple board to develop. Well, our new Breakout Board for microSD Card is the first board that I designed!
Electrically, this board is pretty basic. It breaks out all of the connections available on a microSD card into two rows of 0.1″-spaced pins for easy prototyping use with standard perfboards, solderless breadboards, and 0.1″ connectors. We tried to arrange the pins in a convenient order by placing all of the pins needed for SPI mode on one side of the board (along with the card detect pin). What makes this board interesting mechanically is that it is the first of our products to use a connector for a microSD card. The push-push type connector is positioned so that when a microSD card is fully inserted, it protrudes slightly beyond the edge of the board to allow easy access to the card. The integration of our electrical and mechanical procedures allows us to make 3D models such as the one below to help support our products. We currently use models like this in the dimension diagrams we publish for our boards, but we hope to eventually make the models themselves available too.
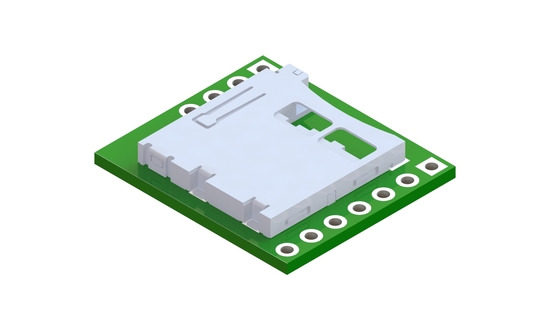 |
Breakout Board for microSD Card rendered in Solidworks. |
|---|
Integration with 5 V systems
There are no other components on the board aside from the microSD card connector. Since standard microSD cards use 3.3 V logic, no extra considerations need to be taken to use it with a 3.3 V microcontroller, but signal conditioning is required for use with 5 V microcontrollers. We did some tests using our 4-channel level shifter and an Arduino Uno to read and write from a microSD card using the Arduino SD library, and we had successful results; however upon closer inspection, we noticed the level shifter did not have time to shift the 3.3 V signals all the way up to 5 V, so this setup only worked because the Arduino Uno registered 3.3 V as a high signal. With a 5 V microcontroller that accepts a 3.3 V signal as high, the microSD card outputs can be connected directly to the microcontroller, and the microcontroller’s 5 V outputs can be shifted to 3.3 V using a simple voltage divider. We found the resistor values needed to be fairly low – we settled on 500 Ω and 1 kΩ resistors. Since we used the standard Arduino SD library, our tests were done at SPI speeds of 4 MHz. In systems operating at higher speeds or with more stringent logic voltage requirements, it might be necessary to use a buffer IC or other high-speed level-shifting solutions.
For more information about this breakout board, see its product page.