Support » Pololu A-Star 32U4 User’s Guide » 4. A-Star 32U4 Mini »
4.4. A-Star 32U4 Mini SV regulators
There have been two versions of the A-Star 32U4 Mini SV: the original ac02c version and its replacement, the newer ac02f version. The ac02f version uses an improved 5 V regulator that can deliver more current (800 mA vs 500 mA) and operates to 40 V instead of 36 V. The easiest way to distinguish between the two versions is via the silkscreen on the side of the board opposite the USB connector, where the original version is labeled ac02c and the new version is labeled ac02f. The new version also uses an ENIG finish, so the plating on the exposed copper looks gold, and it has unplated mounting holes. See the picture below for a side-by-side comparison:
 |
A-Star 32U4 Mini SV: comparison of original ac02c version (left) to newer ac02f version (right). |
|---|
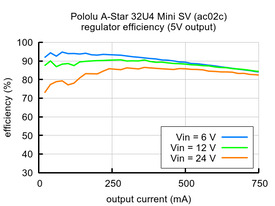
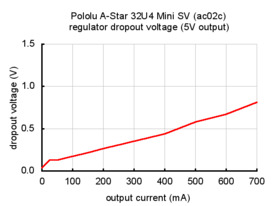
The A-Star 32U4 Mini SV (ac02c) is the original version of the Mini SV, and it can be powered from a 5 V to 36 V external source. The input voltage is regulated to 5 V by a 500 mA ISL85415 switching step-down (buck) converter from Renesas (which acquired Intersil). (We also make a standalone regulator based on this integrated circuit.)
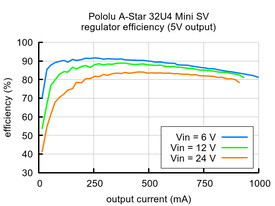
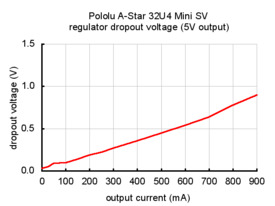
The A-Star 32U4 Mini SV (ac02f) is the newest version of the Mini SV, and it can be powered from a 5 V to 40 V external source. The input voltage is regulated to 5 V by an 800 mA ISL85418 switching step-down converter, which is part of the same family as the ISL85415. (We also make a standalone regulator based on the 1 A version of this integrated circuit.)
The graphs below show the efficiency of the two SV versions, where efficiency is defined as (Power out)/(Power in):
|
|
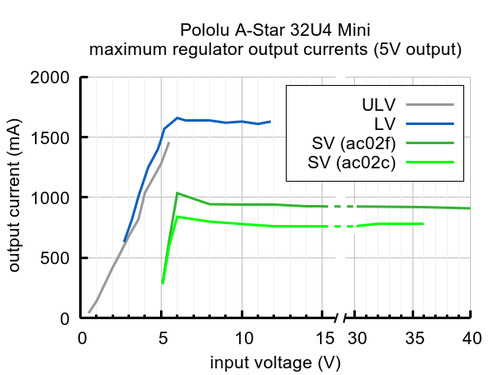
The A-Star’s components, including the microcontroller and LEDs, draw 30 mA to 40 mA in typical applications. The rest of the regulator’s achievable output current, which depends on input voltage as well as ambient conditions, can be used to power other devices. The green lines in the graph below show the output currents where the regulator’s output voltage drops below 4.75 V. These currents are close to the limits of the regulator’s capability and generally cannot be sustained for long periods; under typical operating conditions, a safe limit for the maximum continuous regulator output current is approximately 500 mA for ac02c and 800 mA for ac02f.
 |
The dropout voltage of a step-down regulator is defined as the minimum amount by which the input voltage much exceed the regulator’s target output voltage in order to assure the target output can be achieved. As can be seen in the graphs below for the two versions of the Mini SV, the dropout voltages of the Mini SV’s regulators increase approximately linearly with the output current. For light loads where the dropout voltage is small, the boards can operate down to 5 V. However, for larger loads, the dropout voltage should be taken into consideration when selecting a power supply; operating above 6 V will ensure the full output current is available.
|
|
Note: Batteries can have much higher voltages than their nominal voltages when fully charged, so be careful with nominal voltages above 24 V. A 36 V battery is not appropriate for this product.