Support » Pololu P-Star User’s Guide » 3. P-Star 25K50 Micro »
3.1. P-Star 25K50 Micro pinout and components
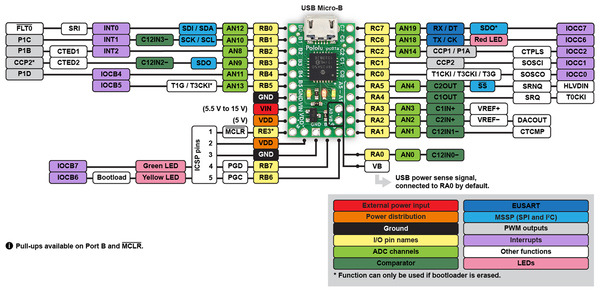 |
P-Star 25K50 Micro pinout diagram. |
|---|
This diagram identifies the I/O and power pins on the P-Star 25K50 Micro. The diagram is also available as a printable PDF (161k pdf). For more information about the PIC18F25K50 microcontroller and its peripherals, see Microchip’s PIC18F25K50 documentation.
LEDs
The P-Star 25K50 Micro has three indicator LEDs. These LEDs are connected in the same way on all P-Stars.
The yellow LED is connected to RB6. Driving this pin high turns on the LED. In bootloader mode, the bootloader drives this line high to turn on the LED (see Section 6.4) but never drives it low. If this line is high when the microcontroller starts up, the microcontroller will go into bootloader mode. A button can be connected to RB6 as described in Section 5.2. RB6 has an on-board pull-down resistor to ensure that its voltage goes all the way down to 0 V when not being driven.
The green LED is connected to RB7, and lights when the pin is driven high. In bootloader mode, the bootloader drives this line high to turn on the LED (see Section 6.4) but never drives it low.
The red LED is connected to RC6, and lights when the pin is driven low. RC6 is the microcontroller’s serial TX line, so the red LED serves as an indicator for when the board is transmitting serial data. If you are not using serial, the LED can be used as a normal LED. To avoid interference with connected serial devices, the bootloader does not use this LED.
Connectors
The P-Star includes a USB Micro-B connector that can be used to connect to a computer’s USB port via a USB A to Micro-B cable (not included). The USB connection can be used to transmit and receive data from the computer, and a preloaded USB bootloader makes it possible to program the board over USB. The USB connection can also provide power to the P-Star.
The board also has five pins arranged so that they can be directly plugged into a standard In-Circuit Serial Programming (ICSP) connector, such as the one found on the PICkit 3. More information about programming with the PICkit 3 can be found in Section 7. The five pins are: MCLR, VDD, GND, RB7/PGD, and RB6/PGC. The MCLR pin is pin 1.
Power
The P-Star 25K50 Micro can either be powered directly from the USB 5 V supply or from a separate source on the VIN pin. The board features a power selection circuit that allows both USB and VIN to be connected at the same time; if this is done, the P-Star will draw power from VIN.
USB power input: The P-Star can be powered from the USB 5 V bus voltage (VBUS) if it is connected to a USB cable. It will draw power from USB only if VIN is disconnected. A resettable PTC fuse on VBUS makes it less likely for the P-Star (and the connected computer or other device) to be damaged if too much current is drawn from the USB connection.
VIN power input: The P-Star can be powered from VIN if you connect a 5.5 V to 15 V power supply (such as a battery or wall power adapter) to the VIN and GND pins, with the positive terminal connected to VIN.
VDD: This pin provides access to the board’s 5 V supply, which comes from either the USB 5 V bus voltage or a low-dropout (LDO) regulator on VIN, depending on which power source is connected. The regulator can supply up to 100 mA, although some of this is used by the board itself or used to provide current for the GPIO pins.
To ensure that VDD is a stable 5 V, you must either disconnect VIN and use USB to power the board or supply a VIN of at least 5.5 V. When VIN drops below 5.5 V, VDD will fall (even with USB connected). However, the P-Star will continue to run with VDD below 5 V, and it can operate from VIN alone with VIN as low as 3.2 V to 3.8 V, depending on the load and temperature. With USB connected, VDD will drop at worst to about 4.5 V, and the P-star will continue operating no matter how low VIN is.
When the P-Star 25K50 Micro is being powered through VIN, regardless of whether USB is connected, the sum of the 5V output current, GPIO output current, and current used by the board itself (typically about 18 mA) should not exceed the 100 mA that the regulator can provide.
|
|
USB power sensing
The VB pin, located on the interior of the board, is connected to the USB 5 V bus voltage through a 1 kΩ resistor. By default, the VB pin is also connected to the RA0 pin through a cuttable trace on the bottom of the board between the two pins. This means that RA0 can be used as a digital or analog input to detect the presence of USB power. Cutting the trace between the VB and RA0 pins allows RA0 to be used for other purposes.
Crystal
The P-Star 25K50 Micro has a precision 16 MHz crystal. By default, this crystal is used to provide a clock signal for the microcontroller and its peripherals.
Included hardware
Two 1×10-pin breakaway 0.1″ male headers and one 1×6-pin breakaway 0.1″ male header are included with the P-Star 25K50 Micro. These header pins can be soldered in to use the board with perfboards, breadboards, or 0.1″ female connectors.
|
|