
This is a merged information page for Item #4761.
View normal product page.
Pololu item #:
4761
Brand:
Pololu
Status:
Active and Preferred

Add quadrature encoders to your micro metal gearmotors (extended back shaft version required) with this kit that uses a magnetic disc and Hall effect sensors to provide 12 counts per revolution of the motor shaft. The sensors operate from 2.7 V to 18 V and provide digital outputs that can be connected directly to a microcontroller or other digital circuit. These encoders have a side-entry, 6-pin male JST SH-type connector, and we have compatible cables available in a variety of lengths.
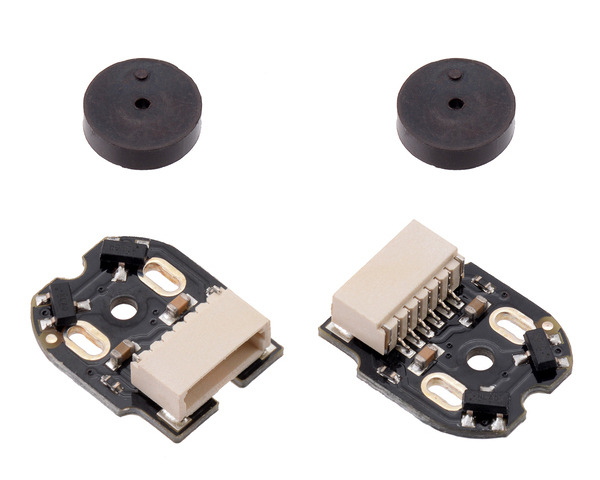
This kit includes two encoder boards and two magnetic discs.
Alternatives available with variations in these parameter(s): connector Select variant…
 Compare all products in Encoders for Micro Metal Gearmotors.
Compare all products in Encoders for Micro Metal Gearmotors.
 |
Magnetic Encoder Pair Kit with Side-Entry Connector for Micro Metal Gearmotors, 12 CPR, 2.7-18V. |
|---|
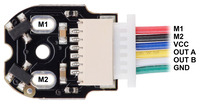 |
Pinout of Magnetic Encoder with Side-Entry Connector for Micro Metal Gearmotors, magnet-side view of PCB with JST cable plugged in (cable not included). |
|---|
 |
Magnetic Encoder with Side-Entry Connector assembled on a Micro Metal Gearmotor with Extended Motor Shaft (JST cable not included). |
|---|
 |
Magnetic Encoder with Side-Entry Connector assembled on a Micro Metal Gearmotor with Extended Motor Shaft (JST cable not included). |
|---|
 |
Magnetic Encoder with Side-Entry Connector for Micro Metal Gearmotors. |
|---|
 |
Magnetic Encoder with Side-Entry Connector for Micro Metal Gearmotors, motor-side view of PCB. |
|---|
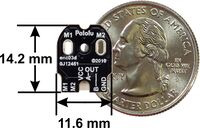 |
Magnetic Encoder with Side-Entry Connector for Micro Metal Gearmotors, 12 CPR, 2.7-18V, motor-side view of PCB with dimensions. |
|---|
 |
Magnetic Encoder with Side-Entry Connector assembled on a Micro Metal Gearmotor with Extended Motor Shaft. |
|---|
 |
Magnetic Encoder with Side-Entry Connector assembled on a Micro Metal Gearmotor with Extended Motor Shaft. |
|---|
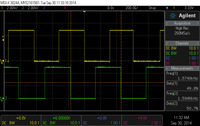 |
A and B outputs of the magnetic encoder on a high-power (HP) 6V Micro Metal Gearmotor running at 6 V. |
|---|
 |
Schematic diagram of the Magnetic Encoder Pair Kit with JST SH-Type Connector (Top-Entry or Side-Entry) for Micro Metal Gearmotors. |
|---|
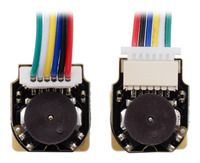 |
Magnetic Encoders with Top-Entry Connector (left) and Side-Entry Connector (right) assembled on Micro Metal Gearmotors with Extended Motor Shafts (JST cables not included). |
|---|
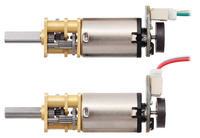 |
Magnetic Encoder with Top-Entry Connector (top) and Side-Entry Connector (bottom) assembled Micro Metal Gearmotors with Extended Motor Shafts (JST cables not included). |
|---|
 |
Side-by-side comparison of Magnetic Encoder with Top-Entry Connector (left), Side-Entry Connector (center), and 2mm-pitch through-holes (right). |
|---|
 |
Magnetic Encoder with Top-Entry Connector (left), Side-Entry Connector (center), and 2mm-pitch through-holes (right) assembled on Micro Metal Gearmotors with Extended Shafts. |
|---|
 |
Magnetic Encoder kit with Top-Entry Connector (top), Side-Entry Connector (center), and 2mm-pitch through-holes (bottom) assembled on Micro Metal Gearmotors with Extended Shafts. |
|---|
 |
Standard packaging for the Magnetic Encoder Pair Kit with Side-Entry Connector for Micro Metal Gearmotors, 12 CPR, 2.7-18V. |
|---|
This kit includes two dual-channel Hall effect sensor boards and two 6-pole magnetic discs that can be used to add quadrature encoding to two micro metal gearmotors with extended back shafts (motors and cables are not included with this kit). The encoder board senses the rotation of the magnetic disc and provides a resolution of 12 counts per revolution of the motor shaft when counting both edges of both channels. To compute the counts per revolution of the gearbox output shaft, multiply the gear ratio by 12. This compact encoder solution fits within the 12 mm × 10 mm cross section of the motors on three of the four sides, and it extends 4.2 mm past the edge of the fourth side.
|
|
The encoders include a side-entry, 6-pin male JST SH-type connector. We also carry a version of this encoder with a top-entry connector; the following pictures show comparisons of the top-entry and side-entry versions:
Note: This sensor system is intended for users comfortable with the physical encoder installation. It only works with micro metal gearmotors that have extended back shafts.
We have two types of cables with matching JST SH-style connectors that can be used with these encoders.
Single-ended cables, with a connector on one end and unterminated wires on the other end, are available in three lengths:
 |
Twisted female-female cables with connectors on both ends are available in five lengths:
 |
These double-ended cables can be used with our JST SH-style connector breakout boards (available in top-entry and side-entry versions) to easily access the motor and encoder pins on a standard solderless breadboard.
|
|
The encoder board is designed to be soldered directly to the back of the motor, with the back shaft of the motor protruding through the hole in the middle of the circuit board. One way to achieve good alignment between the board and the motor is to tack down the board to one motor pin and to solder the other pin only when the board is flat and well aligned. Be careful to avoid prolonged heating of the motor pins, which could deform the plastic end cap of the motor or the motor brushes. Once the board is soldered down to the two terminals, the motor leads are connected to the M1 and M2 connector pins as labeled below, and they can be accessed via the red and black wires when used with our corresponding JST cables. The remaining four connector pins are used to power the sensors and access the two quadrature outputs:
| Pin | Wire color | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Green | encoder GND |
| 2 | White | encoder channel B output |
| 3 | Yellow | encoder channel A output |
| 4 | Blue | encoder Vcc (2.7 V to 18 V) |
| 5 | Black | motor power M2 (other terminal) |
| 6 | Red | motor power M1 (“+” terminal) |
|
|
The sensors are powered through the VCC (blue wire) and GND (green wire) pins. VCC can be 2.7 V to 18 V, and the quadrature outputs A and B (yellow and white wires) are digital signals that are either driven low (0 V) by the sensors or pulled to VCC through 10 kΩ pull-up resistors, depending on the applied magnetic field. The sensors’ comparators have built-in hysteresis, which prevents spurious signals in cases where the motor stops near a transition point.
 |
A and B outputs of the magnetic encoder on a high-power (HP) 6V Micro Metal Gearmotor running at 6 V. |
|---|
 |
This schematic is also available as a downloadable pdf (84k pdf).
This encoder version is a modification of the previous version that adds a connector to enable the use of removable cables. The basic schematic is unchanged, and the electrical performance is identical. The following picture shows the two new encoders with JST SH-type connectors next to the previous (green) one:
 |
Side-by-side comparison of Magnetic Encoder with Top-Entry Connector (left), Side-Entry Connector (center), and 2mm-pitch through-holes (right). |
|---|
| Size: | 14.2 mm × 11.6 mm1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 1.5 g2 |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 2.7 V |
|---|---|
| Maximum operating voltage: | 18 V |
| Connector: | side-entry, 6-pin male, JST SH-type |
| PCB dev codes: | enc03d |
|---|---|
| Other PCB markings: | 0J12461 |
This file contains dimension diagrams for the Magnetic Encoder Pair Kit with Top-Entry Connector and the Magnetic Encoder Pair Kit with Side-Entry Connector.
This file contains 3D models (in the step file format) of the components for the Magnetic Encoder Pair Kit with Top-Entry Connector and the Magnetic Encoder Pair Kit with Side-Entry Connector.
This file contains 3D models (in the step file format) of the for the various versions of the Micro Metal Gearmotors.
These DXF drawings show the locations of all of the holes on the Magnetic Encoder Pair Kit with Top-Entry Connector (enc03c) and the Magnetic Encoder Pair Kit with Side-Entry Connector (enc03d).
No FAQs available.
Micro Metal Gearmotor with 12 CPR encoder, back connector. Micro Metal Gearmotor with 12 CPR encoder, side connector. Our Micro Metal...
We have expanded our selection of JST SH-style cables and connectors! These cables and connectors are ideal for use with our magnetic...
Everyone wants encoders on their motors, but not everyone wants to solder a bunch of wires to a tiny encoder board. That is why I am excited to...