Next:
3.c.
Shield connections: signals, power, and motors
Previous:
3.a.
What you will need
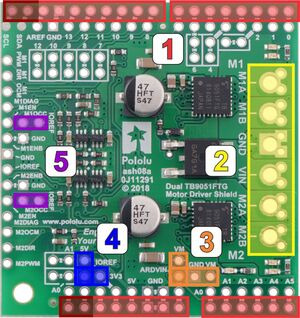 |
- Stackable Arduino headers: Before you can use this board as an Arduino shield, you need to solder four of the five included Arduino header strips to the set of holes highlighted in red in the picture above. The headers should be oriented so that the female sockets rest on the top side of the shield and face up while the male pins protrude down through the board, and the solder connections should be made on the underside of the shield. Newer Arduino boards, including the Uno R3 and the Leonardo, use one 1×10 header, two 1×8 headers, and one 1×6 header, as shown in the picture to the right; older Arduino boards use two 1×8 headers and two 1×6 headers (the two pairs of pins highlighted in darker red above should not be populated if you are using this board with an older Arduino that does not support these additional pins). Please make sure you solder the appropriate headers for your particular Arduino!
- Motor and power connections: The six large holes/twelve small holes on the right side of the board, highlighted in yellow in the above diagram, are the motor outputs and power inputs. You can optionally solder the included 5mm-pitch terminal blocks to the six large holes to enable temporary motor and motor power connections (see our short video on terminal block installation), or you can break off a 1×12 section of the included 0.1″ header strip and solder it into the smaller through-holes that border the six large motor and motor power pads. Note, however, that each header pin is only rated for 3 A (there is a pair of pins for each connection), so for higher-power applications, the terminal blocks should be used or thick wires with high-current connectors should be soldered directly to the board. The smaller holes are intended only for 0.1″ header pins, not for the terminal blocks!
- Arduino power jumper: If you want the option of powering your Arduino and motor shield from the same source, you can use the pins highlighted in orange in the picture above. If your motor power is within the required input voltage range for your Arduino, you can solder a 1×2 piece of the included 0.1″ male header strip to the two adjacent pins labeled VM and ARDVIN. Shorting across these pins with the included shorting block will connect the shield’s reverse-protected power, VM, to the Arduino’s VIN pin. You should not use this to power the shield from the Arduino as this connection is not designed to handle high currents, and you must never supply power to the Arduino’s VIN pin or power jack while this shorting block is in place, because it will create a short between the shield power supply and the Arduino power supply and will likely permanently damage something.
Alternatively, if your motor power is not within the voltage range required for your Arduino, but you would still like to use it to power your Arduino, you can connect a regulator to the 3 pins labeled ARDVIN, GND, and VM (also highlighted in orange) to provide a regulated voltage to the Arduino. Never supply power to the Arduino’s VIN pin or power jack when powering your Arduino this way, because it will create a short between the regulator’s output voltage and the Arduino power supply and will likely permanently damage something.
- Logic voltage: The shield uses the voltage from the Arduino’s IOREF pin for its logic voltage. If your Arduino doesn’t have an IOREF pin, connect the IOREF pin highlighted in blue in the picture above to either the adjacent 5V or 3V3 pin, whichever one corresponds to your Arduino’s logic voltage. You can use a 1×2 piece of the included 0.1″ male header strip and a shorting block to do this.
- M1OCC and M2OCC to IOREF: The M1OCC and M2OCC pins set the drivers’ over-current response. By default, the drivers remain disabled after an over-current condition, but if the OCC pins are high, they automatically try to resume driving after a short delay instead. You can use the pins highlighted in purple to short the M1OCC and M2OCC pins to the IOREF voltage using a 1×2 piece of the included 0.1″ male header strip and a shorting block.
Next:
3.c.
Shield connections: signals, power, and motors
Previous:
3.a.
What you will need





